Briefly Describe the Uses for Antibiotics in Food-producing Animals
Antibiotics have been used in livestock feed since the 1940s when studies showed that the drugs cause animals to grow faster and put on weight more efficiently. 18 The different applications of antibiotics in food animals have been described as therapeutic use prophylactic use and subtherapeutic use.
Since the 1940s antibiotics have.
. Why do farmers use antibiotics in livestock production. Just like humans animals can contract infections such as pneumonia. The use of antibiotics in farmed animal production is an essential tool to combat production diseases improve animal welfare and safeguard food entering the human food chain.
It also recommends phasing in over a period of three years veterinary oversight of all medically important drugs being used. But over 80 of antibiotics used in food animals is put into their feed or water by livestock producers almost always on a herd-wide basis. The FDA has approved antibiotics for only these 3 uses in food animals.
Antibiotics are used in food animals to treat clinical disease to prevent and control common disease events and to enhance animal growth. By killing off the bacteria in the animals guts the antibiotics make more of the energy in the food available for the animals themselves. The most commonly used drug classes in humans and animals are very different.
Antimicrobial resistance is a public health threat. They work by killing or stopping the growth of harmful bacteria. The use of US.
Farms switch baby pigs from milk too soon and use antibiotics to control the stomach bugs that inevitably occur. Antibiotic use in food animals can help treat control and prevent bacterial diseases in animals. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria present in the guts of animals can get in food in several ways.
Because antimicrobial consumption in food-producing animals contributes to the problem policies restricting the inappropriate or unnecessary agricultural use of antimicrobial drugs are important. Antibiotics are medicines useful for controlling and preventing disease in livestock. In the US many livestock producers give their animals low doses of certain antibiotics to improve overall health and help.
Livestock rearing and production methods in which large cohorts of animals are raised in close proximity in feedlots cattle or rearing sheds pigs or poultry. First antibiotics are used to prevent treat and control bacterial infections in livestock. An estimated 60 percent of all medically important antibiotics are sold for use on farm animalsnot only to treat disease but also to compensate for crowded stressful and unhealthy conditions.
This makes animals put on weight faster even if they. Approximately 70 percent of the volume of antibiotics used in animals are ionophores and tetracyclines. 14 Because of this growth advantage non-therapeutic antibiotics those.
However there are overriding concerns regarding their use in both animals and particularly humans where the spectre of highly resistant pathogens defy treatment have emerged. However to slow the spread of antibiotic resistance antibiotics should only be. The use of some antibiotics can destroy certain bacteria in the gut and help livestock and poultry convert feed to muscle more quickly causing more rapid growth.
Food and Drug Administration FDA approved antibiotics help to keep animals healthy but their use is limited in order to ward off the incidence of antibiotic resistant bacteriawhich can be a problem for animals people and the environment. Such antibiotics are known as medically important antimicrobial drugs. In Australia antibiotic substances are added to animal feed for therapeutic prophylactic growth promotion and anticoccidial purposes.
Antibiotic use in food-producing animals Antibiotics are drugs used to treat bacterial infections. Livestock producers routinely give antibiotics to animals to make them grow faster or help them survive crowded stressful and unsanitary conditions. Disease treatment for animals that are sick.
2 Briefly describe the uses for antibiotics in food-producing animals. Animals like people carry bacteria in their guts. An important point here.
Antibiotics are used in food animals to help promote animal health by treating diseases caused by bacterial infection either by killing the bacteria or making it difficult for them to grow and multiply. Antibiotics can be used to treat a single animal with clinical disease or a large group of animals. It should be noted that there were some fairly sweeping changes that went into effect in 2017 as part of an effort to promote the judicious use of medically-important antimicrobial drugs in food animals.
The Judicious Use of Medically Important Antimicrobial Drugs in Food-Producing Animals recommends that food animal producers voluntarily phase out the use of medically important drugs for growth promotion or feed efficiency. Ionophores arent used in human. 2 Briefly describe the uses for antibiotics in food-producing animals.
Proper use can keep animals healthy control the spread of diseases between herds help animals gain weight and prevent the spread of diseases from animals to humans. Nutrition 1 Janice is watching the Tour de France and hears that some cyclists are being accused of blood doping. When animals are slaughtered and processed for food resistant bacteria can contaminate meat or other animal products.
However this link between agricultural antibiotic use and antibiotic resistance has remained contested by. According to the American Meat Institutes The Facts About Antibiotics in Livestock Poultry Production.

Why We Should Reduce Antibiotic Usage And Ways To Do It The Pig Site

Global Antimicrobial Use In Food Animals A Major Users Of Download Scientific Diagram
Pdf Critically Important Antibiotics Criteria And Approaches For Measuring And Reducing Their Use In Food Animal Agriculture
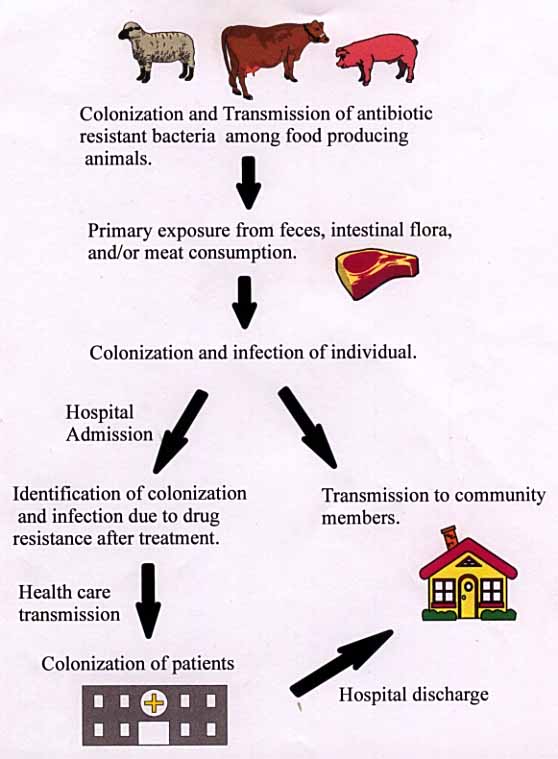
Effects Of Antibiotics On Animal Feed Presentation

Why We Should Reduce Antibiotic Usage And Ways To Do It The Pig Site
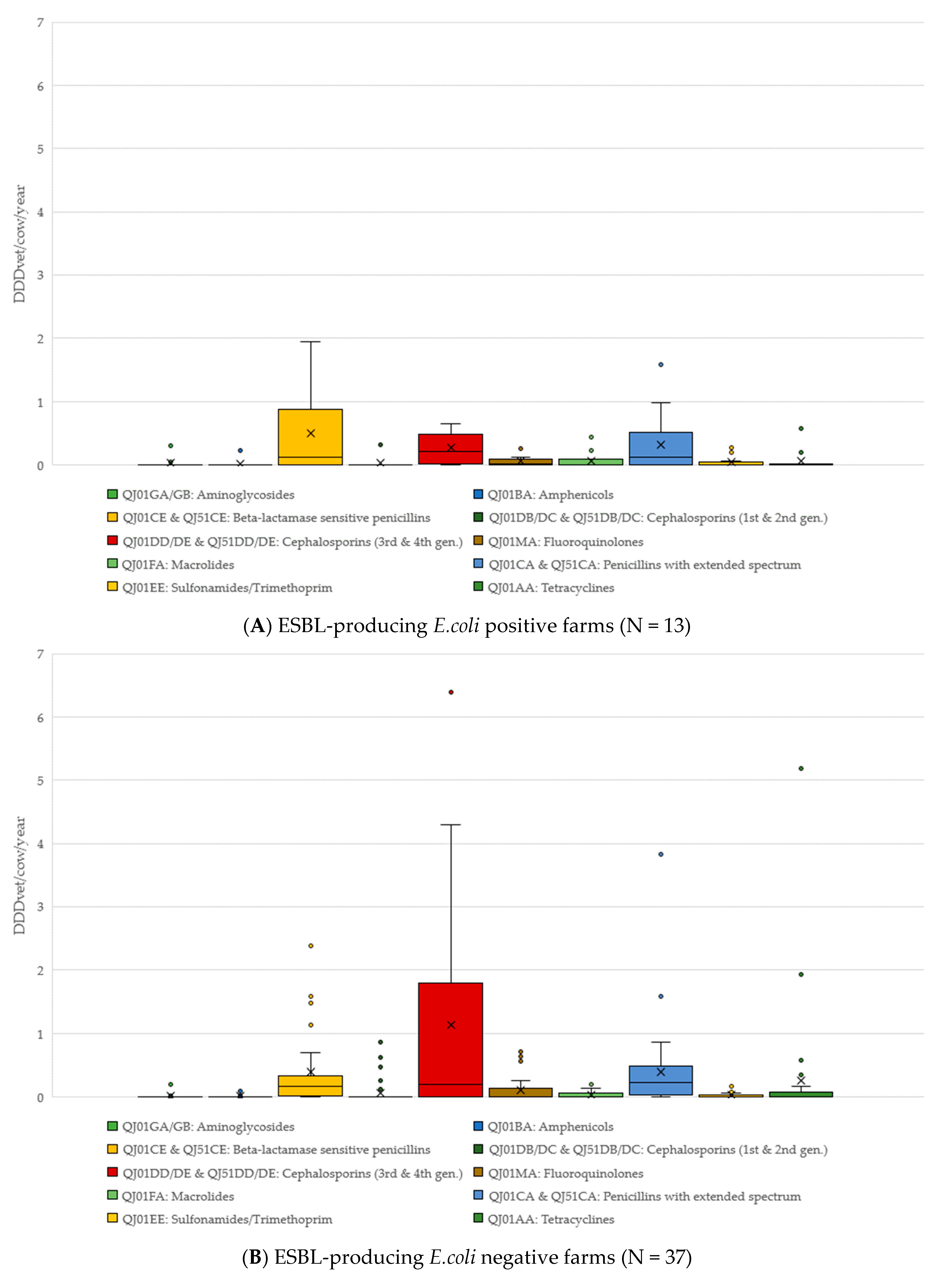
Antibiotics Free Full Text Analysis Of Antimicrobial Use And The Presence Of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria On Austrian Dairy Farms A Pilot Study Html
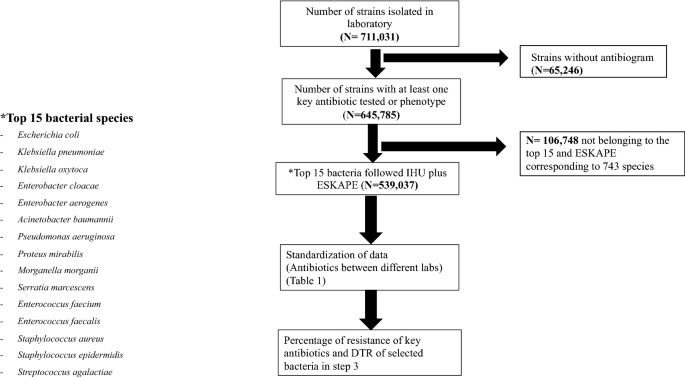
Major Discrepancy Between Factual Antibiotic Resistance And Consumption In South Of France Analysis Of 539 037 Bacterial Strains Scientific Reports
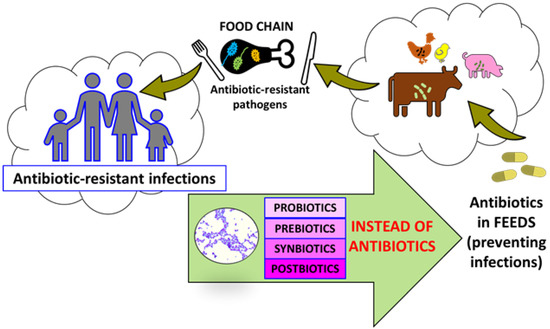
Animals Free Full Text Probiotics And Postbiotics As Substitutes Of Antibiotics In Farm Animals A Review Html

Antibiotics Free Full Text Factors Associated With Antimicrobial Stewardship Practices On California Dairies One Year Post Senate Bill 27 Html
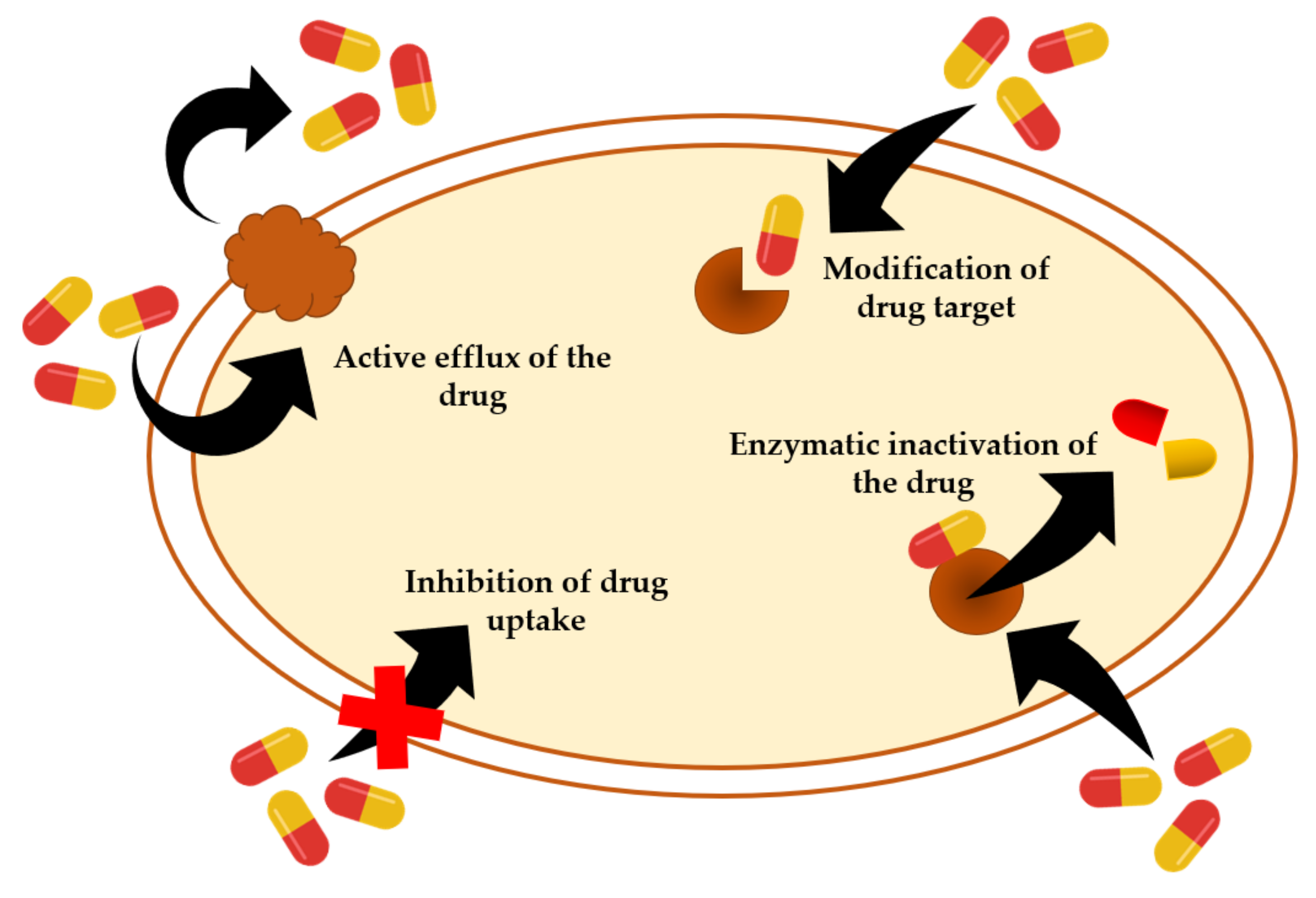
Animals Free Full Text Bacterial Skin Infections In Livestock And Plant Based Alternatives To Their Antibiotic Treatment Html

The Political Economy Of Us Antibiotic Use In Animal Feed Springerlink
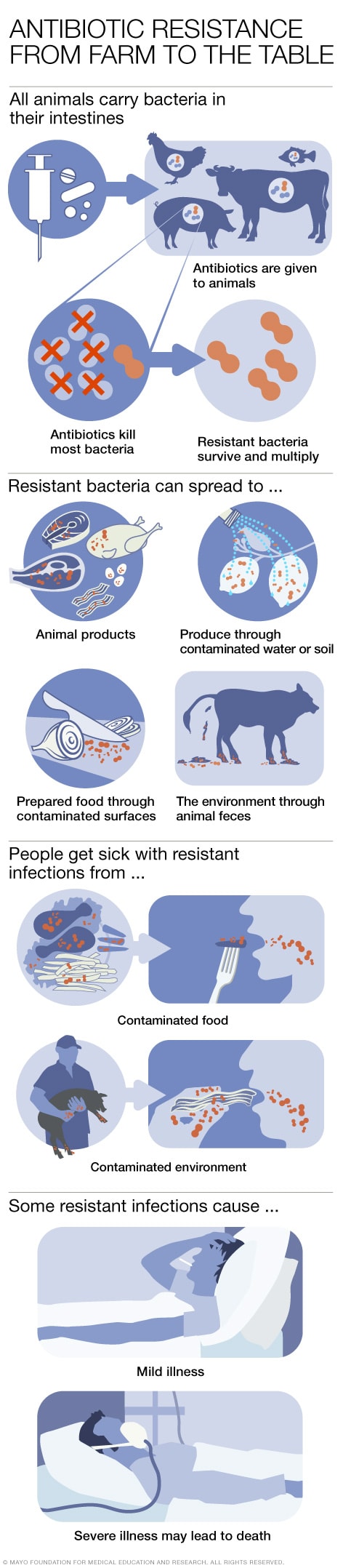
Antibiotic Resistance Understanding The Connection To Antibiotic Use In Animals Raised For Food Mayo Clinic

Why We Should Reduce Antibiotic Usage And Ways To Do It The Pig Site
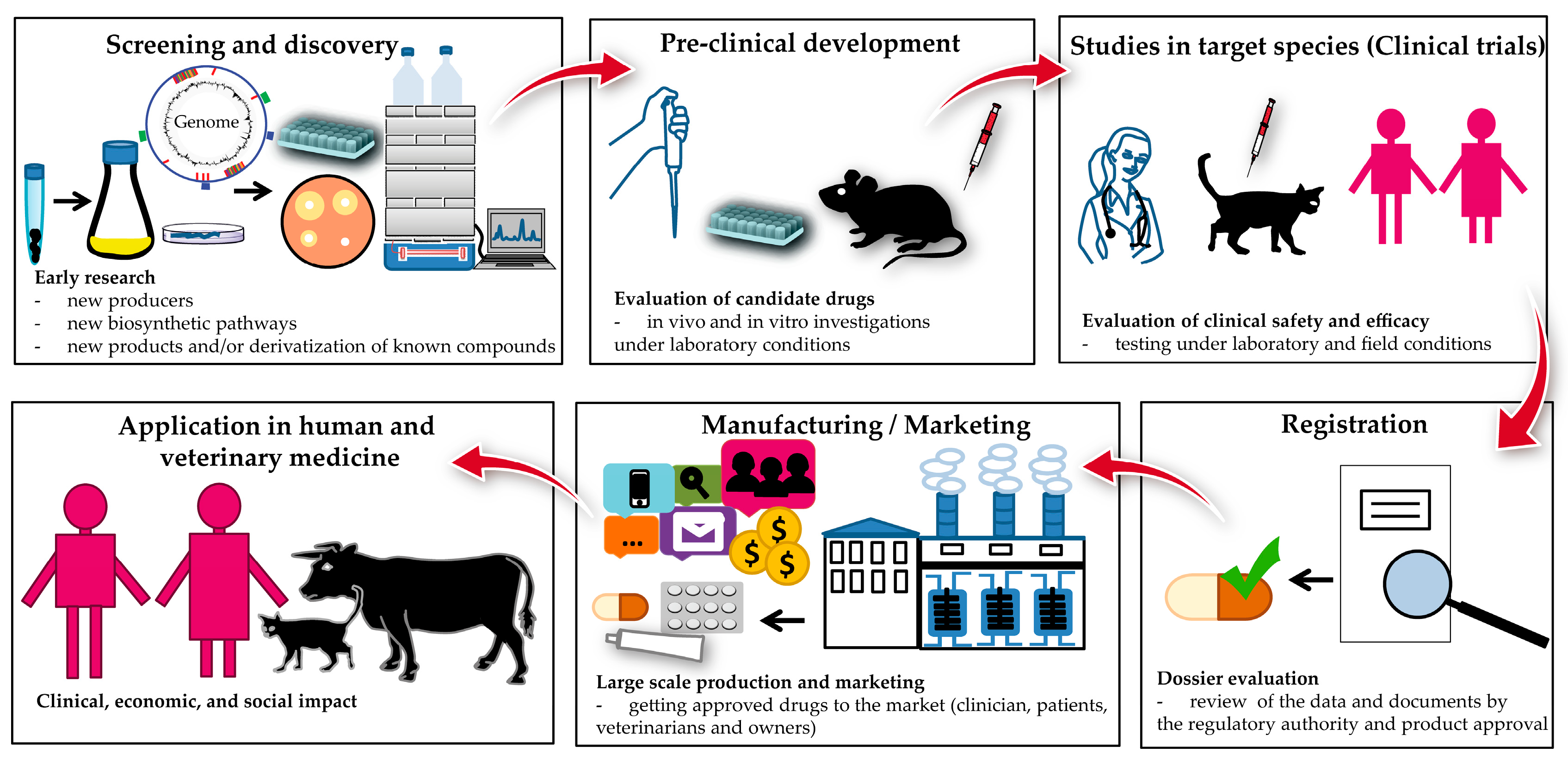
Antibiotics Free Full Text Actinomycete Derived Polyketides As A Source Of Antibiotics And Lead Structures For The Development Of New Antimicrobial Drugs Html
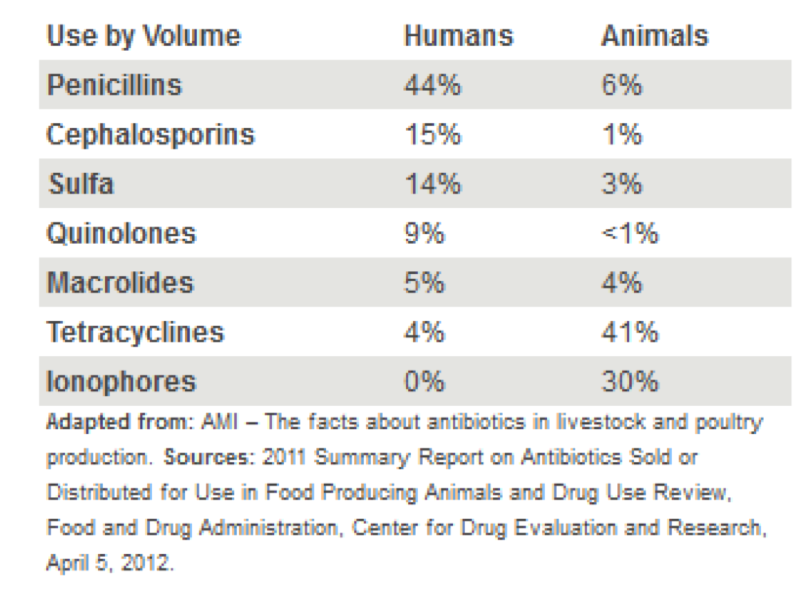
Hormones And Antibiotics In Animal Production North Carolina Cooperative Extension

Why We Should Reduce Antibiotic Usage And Ways To Do It The Pig Site

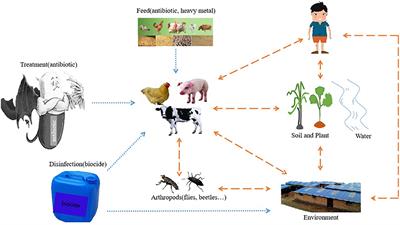
Frontiers The Influencing Factors Of Bacterial Resistance Related To Livestock Farm Sources And Mechanisms Animal Science

Why We Should Reduce Antibiotic Usage And Ways To Do It The Pig Site

Why We Should Reduce Antibiotic Usage And Ways To Do It The Pig Site